Conversely, a current ratio that is lower than industry norms may be a risky strategy that could entail liquidity problems for the company. It must be analyzed in the context of the industry the company primarily relates to. The underlying trend of the ratio must also be monitored over a period of time.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
Finally, the operating cash flow ratio compares a company’s active cash flow from operating activities (CFO) to its current liabilities. This allows a company to better gauge funding capabilities by omitting implications created by accounting entries. The current ratio can be a useful measure of a company’s short-term solvency when it is placed in the context of what has been historically normal for the company and its peer group. It also offers more insight when calculated repeatedly over several periods. A current ratio that is in line with the industry average or slightly higher is generally considered acceptable.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- Some industries are seasonal, and the demand for their products or services may vary throughout the year.
- Analysts also must consider the quality of a company’s other assets vs. its obligations.
- Current liabilities include accounts payable, wages, accrued expenses, accrued interest and short-term debt.
- The current ratio or working capital ratio is a ratio of current assets to current liabilities within a business.
- The current ratio is a rough indicator of the degree of safety with which short-term credit may be extended to the business.
However, the end result of the calculation could mean different things based on the result. Let us understand how to interpret the data from a current ration calculator through the discussion below. Larger companies may have a lower current ratio due to economies of scale and their ability to negotiate better payment terms with suppliers. Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products.
Increase Sales and Revenue – Ways a Company Can Improve Its Current Ratio
So, a ratio of 2.65 means that Sample Limited has more than enough cash to meet its immediate obligations. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.

But, during recessions, they flock to companies with high current ratios because they have current assets that can help weather downturns. You calculate your business’s overall current ratio by dividing your current assets by your current liabilities. In simplest terms, it measures the amount of cash available relative to its liabilities. The current ratio expressed as a percentage is arrived at by showing the current assets of a company as a percentage of its current liabilities. However, if the current ratio of a company is below 1, it shows that it has more current liabilities than current assets (i.e., negative working capital). If the current ratio of a business is 1 or more, it means it has more current assets than current liabilities (i.e., positive working capital).
Decrease In Current Assets – Common Reasons for a Decrease in a Company’s Current Ratio
The quick ratio focuses on assets that can be converted to cash quickly, such as cash reserves and receivables, and shows your company’s financial flexibility and resilience. However, if you learned this skill through other means, such as coursework or on your own, your cover letter is a great place to go into more detail. For example, you could describe a project you did at school that involved evaluating a company’s financial health or an instance where you helped a friend’s small business work out its finances.
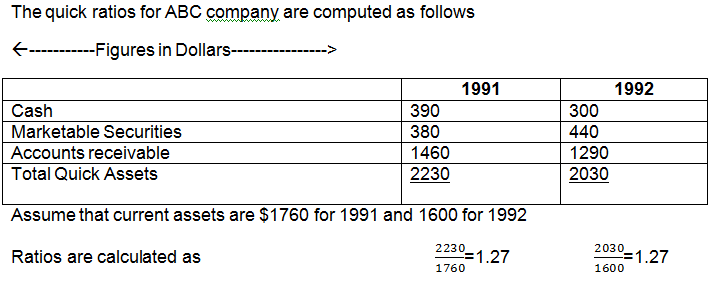
What counts as a good current ratio will depend on the company’s industry and historical performance. Current ratios over 1.00 indicate that a company’s current assets are greater than its current liabilities, meaning it could more easily pay of short-term debts. A current ratio of 1.50 or greater would generally indicate ample liquidity. It is important to note that a similar ratio, the quick ratio, also compares a company’s liquid assets to current liabilities.
Businesses must also plan for solvency, which is the company’s ability to generate future cash inflows. Solvency is required to pay for capital expenditures, such as equipment, machinery, and other expensive assets needed to run the business. However, if you look at company B now, it has all cash in its current assets. Therefore, even though its ratio is 1.45x, strictly from the short-term debt repayment perspective, it is best placed gocardless as it can immediately pay off its short-term debt. Businesses must analyze their working capital requirements and the level of risk they are willing to accept when determining the target current ratio for their organization. A current ratio that is higher than industry standards may suggest inefficient use of the resources tied up in working capital of the organization that may instead be put into more profitable uses elsewhere.
A high current ratio can make it easier for a company to obtain credit, while a low current ratio may make it more difficult to secure financing. Creditors and lenders also use the current ratio to assess a company’s creditworthiness and determine whether or not to extend credit. A high current ratio can make it easier for a company to obtain credit, while a low current ratio may make it more challenging to secure financing. Current liabilities refers to the sum of all liabilities that are due in the next year. The volume and frequency of trading activities have high impact on the entities’ working capital position and hence on their current ratio number.
This is because excess cash and inventory do not generate returns like investments in new projects or debt repayments can. A high current ratio can signal that a company is not taking advantage of investment opportunities or paying off its debts promptly. This can lead to missed opportunities for growth and potential financial difficulties down the line. For example, companies in industries that require significant inventory may have a lower quick ratio but still have a good current ratio. Lenders and creditors also use the current ratio to assess a company’s creditworthiness.
A higher current ratio indicates strong solvency position of the entity in question and is, therefore, considered better. The quick ratio (also sometimes called the acid-test ratio) is a more conservative version of the current ratio. Current assets refer to cash and other resources that can be converted into cash in the short-term (within 1 year or the company’s normal operating cycle, whichever is longer). Note the growing A/R balance and inventory balance require further diligence, as the A/R growth could be from the inability to collect cash payments from credit sales. The limitations of the current ratio – which must be understood to properly use the financial metric – are as follows. The current ratio reflects a company’s capacity to pay off all its short-term obligations, under the hypothetical scenario that short-term obligations are due right now.
