
More in detail, its value and, most importantly, its trend can help us predict the company’s future financial situation and see if it will go through stability or likely bankruptcy. On a corporate level, companies can go to the stock exchange to sell a percentage of their ownership in return for cash. If the TIE ratio is exactly 1, it means the company’s EBIT is just enough to cover its interest expenses, leaving no room for error or additional financial strain.
What is time interest earned ratio?
So long as you make dents in your debts, your interest expenses will decrease month to month. But at a given moment, this amount can be hundreds or thousands of dollars piling onto your plate, in addition to your regular payments and other business expenses. The times interest earned formula is calculated on your gross revenue that is registered on your income statement, before any loan or tax obligations. The ratio is not calculated by dividing net income with total interest expense for one particular accounting period. It is only a supporting metric of the financial stability and cash arm of your business which determines that you have the ability to clear off your liabilities with whatever you earn.
Rule of 72 Calculator – Calculate Compound Interest
What’s more, higher disposable income means that you are in a better position for growth. This is because you can invest in new equipment or expand. Obviously, when you have the operating expenses to reinvest in your business, it shows you are performing well. When the times earned interest ratio is comfortably above 1, you can feel confident that the firm you’re evaluating has more than enough earnings to support its interest expenses. This can be interpreted as a high-risk situation since the company would have no financial recourse should revenues drop off, and it could end up defaulting on its debts. This example illustrates that Company W generates more than three times enough earnings to support its debt interest payments.
Bps To Percent Calculator – Basis Points to Percentage Conversion
In doing so, you can get a good idea as to how well your business is doing. The times interest earned ratio, sometimes called the interest coverage ratio, is a coverage ratio that measures the proportionate off balance sheet definition amount of income that can be used to cover interest expenses in the future. The deli is doing well, making an average of $10,000 a month after expenses and before taxes and interest.
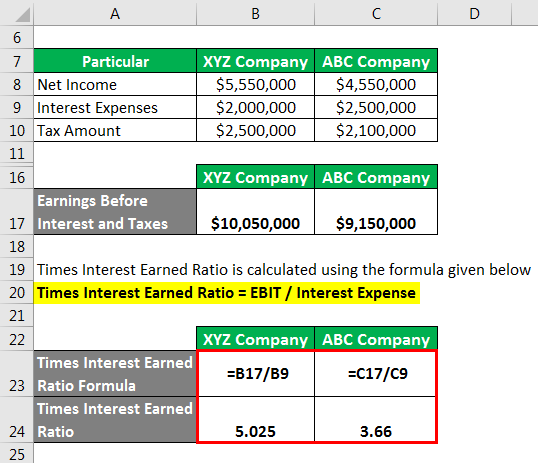
Formula and Calculation of the Times Interest Earned (TIE) Ratio
For that reason, it is essential to have a broad understanding of the business and how it is performing financially. That’s why we highly recommend you check our other financial calculators. Startup firms and businesses that have inconsistent earnings, on the other hand, raise most or all of the capital they use by issuing stock. Once a company establishes a track record of producing reliable earnings, it may begin raising capital through debt offerings as well.
How Can a Company Improve Its Times Interest Earned Ratio?
The times interest earned (TIE) formula was developed to help lenders qualify new borrowers based on the debts they’ve already accumulated. It gave the investors an idea of shareholder’s equity metric and interest accumulated to decide if they could fund them further. So you now know the TIE ratio formula, let’s consider this example so you can understand how to find times interest earned in real life.
A TIE ratio of 2.5 or higher is generally considered good, as it shows that the company can cover its interest expenses multiple times over. A low TIE ratio suggests that the company may struggle to cover its interest expenses, indicating higher financial risk. Assume, for example, that XYZ Company has $10 million in 4% debt outstanding and $10 million in common stock. The company needs to raise more capital to purchase equipment. The cost of capital for issuing more debt is an annual interest rate of 6%.
Conversely, a lower TIE ratio may signal financial distress, where the company struggles to manage its interest payments, posing a higher risk to creditors and investors. In some respects the times interest ratio is considered a solvency ratio because it measures a firm’s ability to make interest and debt service payments. Since these interest payments are usually made on a long-term basis, they are often treated as an ongoing, fixed expense. As with most fixed expenses, if the company can’t make the payments, it could go bankrupt and cease to exist. You can’t just walk into a bank and be handed $1 million for your business.
- As you can see, creditors would favor a company with a much higher times interest ratio because it shows the company can afford to pay its interest payments when they come due.
- Calculating the Times Interest Earned Ratio is crucial for assessing a company’s ability to cover its interest payments with its earnings.
- The metric uses interest payments because they are long-term fixed expenses.
- Here’s a breakdown of this company’s current interest expense, based on its varied debts.
If you have a $10,000 line of credit with a 10 percent monthly interest rate, your current expected interest will be $1,000 this month. If you have another loan of $5,000 with a 5 percent monthly interest rate, you will owe $250 extra after the interest is processed. Your total interest expense for this month, then, is $1,250.
